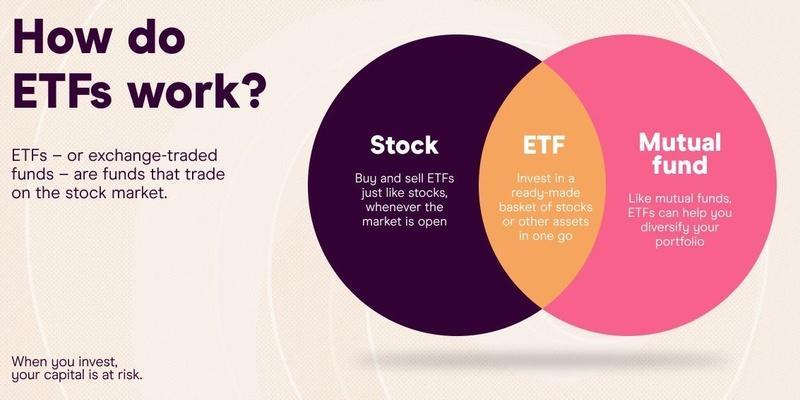
Etf is an efficient investment security that has similarities with the mutual fund. The same is why people usually confuse it with a mutual fund, thinking of both as two different names of the same thing. However, let us be clear that both services are entirely different from each other and obtain distinguished entities.
So, what is an ETF? And How does it work? If you are also searching for the same kind of information, look no further, as we have your back. Keep reading; the forthcoming content will elaborate on an ultimate guide about how ETFs work. So, without any further discussion, let's start with the content.
All you need to know about ETF: What is it? And How does it work?
What is an ETF?
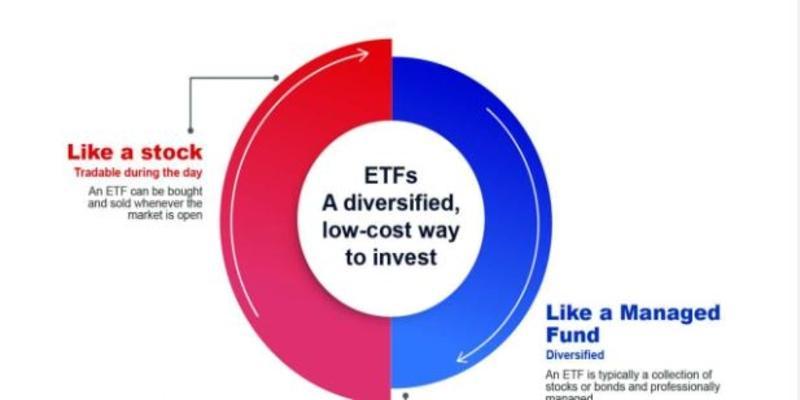
The ETF is a short form of Exchange-traded fund. It is a pooled investment security that keeps track of specific indexes, commodities, and assets. However, unlike other types of mutual funds, an ETF can be bought or sold the same way as regular stock trading. The price can be changed throughout the trading day as per the selling and purchasing ratio. In addition, one can also structure the ETF to trace anything.
This could be an extensive range of commodities or just an individual security. In addition, it can also be structured to track any specific strategies related to investment. The first ETF in history is known as the SPDR S&P ETF. It could follow the S&P Index, which is still used in trading. One major thing that differentiates an ETF from other funds is that you offer way lower expense ratings and broker commissions while purchasing the stocks individually.
Types of ETF
There is an extensive range of ETFs available in the market for investors. These might be used in price enhancement, income generation, edging, or speculations. Here are some of the descriptions of ETFs available today
1: Active and Passive ETF
The ETFs are typically categorized as active or passively managed. The passive ones work with the prime objective of replicating the performance of a broader index. These are either diversified indices such as the S&P 500. Or they might be more specifically targeted to sectors or trends. One of the significant examples of the category is Gold Mining Stocks.
As of December 2023, about 9 ETFs focused on the companies engaged in gold mining practices. Thus excluding the inverse and leveraging with low assets.
On the other hand, the active ETFs are not concerned with a security index. Instead, they obtain a portfolio of securities and data for making timely decisions. These funds comprise the benefits over the passive. Thus, these are typically more expensive than to investors.
2: Bonds ETF
It is a type of actively managed ETF. The investor uses the bond ETF to arrange a regular income stream. This might get distributed in some cases depending upon the performance of the underlying bonds. This includes government bonds, state-local bonds, and corporate bonds. These types of ETFs do not have any maturity dates. Instead, you can trade these at a premium or discount from the actual bond price.
3: Stock ETF
These ETFs have a stock basket to tackle a sector or even a single industry. For instance, the stock ETF can track automotive or foreign stocks without issues. In addition, it also provides diversified data and explores the industry, including the high performers and new entrances.
4: Leveraged ETF
The Leveraged ETFs focus on returning multiples of the underlying investment. The products are derivatives, such as options or futures contracts, necessary to leverage the returns.

5: Inverse ETFs
The inverse ETFs help to earn profit from stock declining and shorting stocks. For those who don't know what a shorting stock is, it refers to selling a stock and expecting a decline in its value. Thus repurchasing it at a lower price.
These types of stocks also rely upon predicting when and at what rate the market will go down.
How do ETFs work?
The financial instrument symbolizes the collection of assets such as financial instruments, stocks, bonds, and other commodities. Hence, the primary mechanism depends upon the creation and redemption process. It involves the authorized participants and creates new shares by depositing the assets with the fund's manager.
When these participants want to redeem their shares, they can return the ETF to their fund manager.
In addition, the investors can purchase or sell the ETF shares on the secondary market using brokerage accounts. Thus proffering enhanced liquidity and flexibility. The ETFs are also considered a cost-effective way to gain exposure to investors. Hence, it establishes itself as a highly efficient source of market exposure for specific investors.
Things to consider while looking for an ETF
Following are some efficient aspects you must consider while purchasing an ETF.
- Volume: looking for a trading volume within a specified time allows comparing the popularity of different funds. Remember, the higher the trading volume is, the easier it might be to trade.
- Expense: Look for as low expense ratios as you can. This will help you maintain a strong and consistent income stream for extended periods.
- Performance: Past performance is another standard metric. These not only provide data about the past but also help to predict future performances.
- Holdings: The portfolios of different funds help compare the various holdings of each investment.
- Commissions: Last but not least, look for the lower fesses. There are also entirely commission-free services. That means you will be allowed to trade without fees. However, there might be some hidden charges involved. So look carefully.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, an ETF is one of the most efficient investment securities one can consider. However, before proceeding, it is vital to understand what it is and how it works. The same is why we have formed this guide, talking about all the relevant information while converting all the significant types. So make sure to read from start to finish.




